Django Manage Commands Cheat Sheet
A short cheat sheet for those who are familiar with Django, and need some reminder for useful Django commands
Installations
In order to get started with Django, all you need to do is install Django package using pip:
pip install django
After the installation is complete, you can move forward and create your Django application.
Django Application creation
Creating a new Django web application consists of two stages:
First, you need to create a new Django project:
django-admin startproject my_project
Note: my_project is a custom name for your project
After running this command, a new folder tree similar to the following will be created:
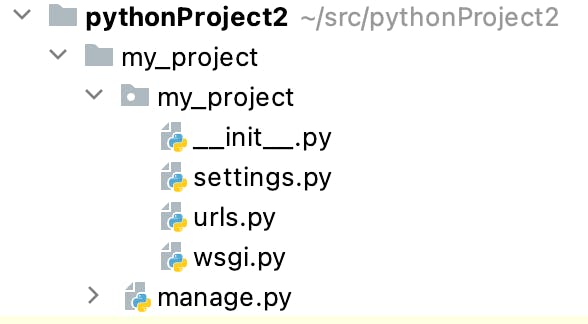
Second, you need to create a new Django application that will sit inside the newly created project. In order to do this, you need to change directory to my_project (the one where manage.py file resides):
cd my_project
python manage.py startapp my_app
Note: my_app is a custom name for your application
After running this command your project tree will look similar to this:
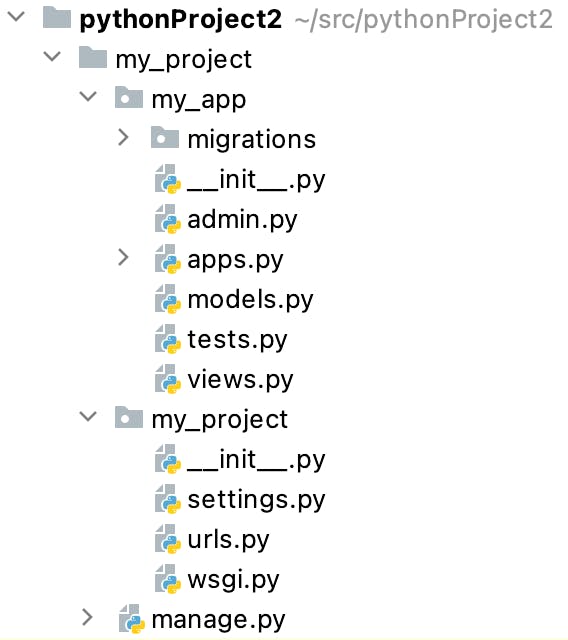
DB management
Create migration
(this should be run after you make changes to your models.py):
python manage.py makemigrations
This command will result in creating a new migration file in your migrations folder:

SQL Migrate
(Review SQL queries that will actually run on your DB server during migrate)
python manage.py sqlmigrate my_app 0001
Note: my_app and 0001 are your app name and migration name respectively
Migrate
(this should be run when you want to apply changes in your migration files on your DB)
python manage.py migrate
Other useful commands
Create superuser
Use this command in order to create superuser that will allow you to login into Django Admin App
python manage.py createsuperuser
Django Shell
Use this command to start Django Shell with your application and models loaded (very useful when you want to play with Django models a bit)
python manage.py shell
Django has loaded your Django application for you, so now you can play with your Django models in Python shell!

